Industrial 3D printing materials encompass a diverse range of substances tailored to meet the demanding requirements of manufacturing, aerospace, automotive, medical, and other industrial sectors. These materials are selected based on their mechanical properties, heat resistance, chemical stability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness to produce functional parts, prototypes, and end-use components with complex geometries.
Common Industrial 3D Printing Materials
Plastics
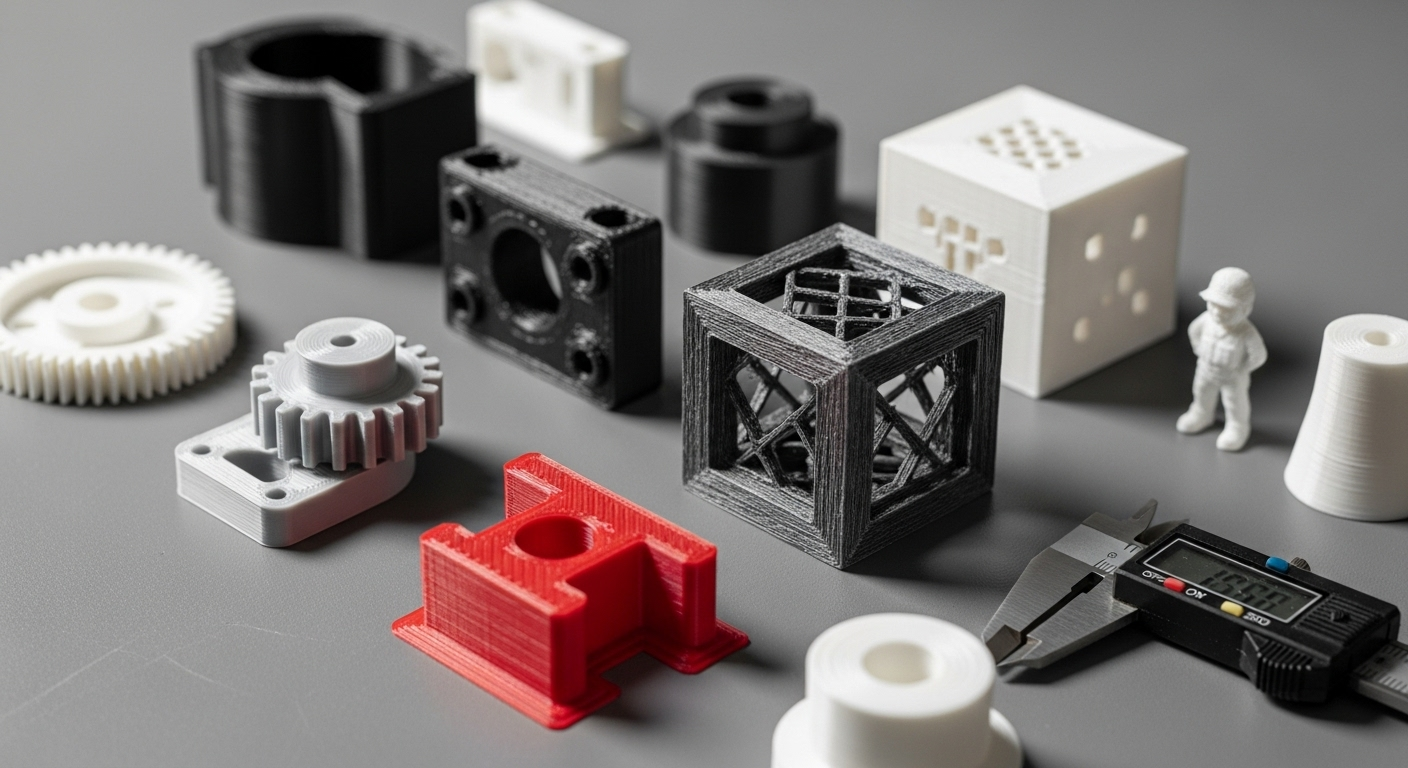
Plastics are among the most widely used materials in industrial 3D printing due to their versatility, lightweight nature, and cost efficiency. Key plastics include:
-
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): Tough and heat-resistant, suitable for functional prototypes and end uses where durability is essential. Requires heated beds and ventilation during printing.
-
PLA (Polylactic Acid): Biodegradable, easy to print, ideal for concept models and visual prototypes, though less heat-resistant and durable than ABS.
-
Nylon (PA12): Known for high strength, flexibility, and abrasion resistance, widely used in automotive, aerospace, and medical applications. Offers low water absorption and impact resistance.
-
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol): Chemically resistant, water-resistant, and suitable for snap-fit components and waterproof applications.
-
ASA (Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate): Similar to ABS but with better UV and weather resistance, making it ideal for outdoor applications and tools.
-
TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane): Flexible, impact-resistant, and vibration-damping, used for flexible prototypes and parts requiring elasticity.
Composites
Composite materials combine plastics with reinforcements like carbon fiber, Kevlar, or fiberglass to enhance strength, stiffness, and durability while keeping parts lightweight. They are valuable in aerospace, automotive, and sporting goods but tend to be more expensive and require specialized printers.
Metals
Metal 3D printing is critical for producing highly durable, heat-resistant, and precise parts, especially in aerospace, automotive, and medical fields. Common industrial metals include:
-
Stainless Steel (e.g., 316L): Corrosion-resistant, strong, and precise, used for functional and structural parts.
-
Titanium: High strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, ideal for aerospace and medical implants.
-
Aluminum: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and good machinability for lightweight parts.
-
Inconel: A high-strength, corrosion-resistant nickel-based alloy suited for aerospace and military applications exposed to extreme temperatures.
Ceramics
Ceramic materials provide excellent heat and chemical resistance and are used in aerospace and industrial applications requiring intricate shapes. However, ceramics can be brittle and require careful post-processing.
Industrial Applications and Considerations
-
Functional Prototypes: Materials like ABS, Nylon, and composites allow testing of parts under real-world conditions.
-
End-Use Parts: Metals (stainless steel, titanium) and high-performance plastics (PEEK, PEKK) are chosen for durability and resistance to harsh environments.
-
Tooling and Fixtures: Composite materials and plastics with good machinability support the production of jigs, molds, and fixtures.
-
Sustainability: Biodegradable options like PLA are gaining attention for reducing environmental impact in prototyping.
Summary Table of Key Industrial 3D Printing Materials
| Material | Key Features | Typical Industrial Applications |
|---|---|---|
| ABS | Tough, heat and impact resistant | Functional prototypes, durable parts |
| PLA | Biodegradable, easy to print | Concept models, visual prototypes |
| Nylon (PA12) | Strong, flexible, abrasion-resistant | Automotive, aerospace, medical parts |
| PETG | Chemical and water-resistant | Waterproof components, snap-fit parts |
| Composite (CF, Kevlar) | High strength, lightweight | Aerospace, automotive, sporting goods |
| Stainless Steel | Corrosion-resistant, strong | Structural parts, medical, automotive |
| Titanium | High strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion-resistant | Aerospace, implants |
| Inconel | High temperature and corrosion resistance | Aerospace, military equipment |
| Ceramic | Heat and chemical resistance | Aerospace, industrial components |
Industrial 3D printing materials continue to evolve, with ongoing advancements enhancing their mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties. Choosing the right material depends on the specific application requirements, desired part properties, and production methods such as FDM, SLS, DMLS, or binder jetting.



Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.